Exploring the Earth Fault Protection System
The Earth Fault Protection System refers to safety measures that lessen electrocution risks.
This system detects any deviation from the intended electrical pathway. When it senses a fault, it promptly disconnects the electrical supply, safeguarding both equipment and personnel.
Read on to learn more of its practical applications.

Table of Contents
the Ground Fault Protection System
Defining Ground Fault Protection System
The ground fault protection system is a technological mechanism primarily designed to ensure safety by preventing electrical shocks resulting from ground faults.
A ground fault occurs when an undetermined amount of electric current escapes the established path of an electrical system.
A Closer Look at Ground Faults
When there is a breach in the insulation of an electrical wire that enables the electric current to take an unintended path to the ground, a ground fault arises.
This occurrence can cause severe electrical shocks if a person comes into contact with an object energized by such a current.
How Does the Ground Fault Protection System Work?
The ground fault protection system works by constantly monitoring the balance of electrical currents in a circuit. In the event of a ground fault, the system recognizes the loss of current, disturbs the sense of equilibrium, and automatically disconnects the faulty circuit.
Key Components of a Ground Fault Protection System
- Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI): This device immediately shuts off an electrical power circuit when it detects that current is flowing along an unintended path, such as through water or a person.
- Circuit breaker: A switch device that disconnects the faulty circuit when it detects an excess current flow due to a ground fault.
- Grounding conductor: Basically a backup pathway, the grounding conductor offers an alternative path for the electricity to flow back to the ground to avoid causing damages or injuries.
The Importance of Ground Fault Protection Systems in Construction
In the construction industry, the safety of workers handling electrical equipment is of utmost priority. Therefore, ground fault protection systems play a critical role in construction sites.
- Enhances the safety of the construction site
- Reduces risk of electrical shock
- Decreases the likelihood of fires caused by grounding faults
- Saves costly equipment from getting damaged
Exploring the Dangers of Ground Faults
Having a closer look at the hazards associated with these ground faults is fundamental to the realm of construction. Employing a ground fault protection system can shield from electrifying threats, but first, let’s understand the risks precisely.
Potential Hazards of Ground Faults
Ground faults pose several significant threats, not only to the safety of individuals working within these electrical environments but also to the overall system’s performance. When an electrical circuit is redirected to an unintended path, this can lead to a myriad of negative consequences.
Electric Shocks and Electrocution
As already touched on, one of the most prevalent hazards from ground faults is the risk of electric shocks – sometimes severe enough to cause electrocution.
This hazardous electric current can be transferred to a person who touches a conductive object or material energized by the escaped current. This poses a serious risk to construction workers who frequently engage with electrical systems.
Fire Risk
Ground faults can become a potential fire hazard. When electrical current flows along an unintended path, it can lead to heat buildup and potentially start a fire. This risk is particularly greater in environments with flammable materials – typically any construction site.
System Damage
Ground faults can have serious implications for electrical system integrity. They can damage insulation, overheat circuits, and even corrode or deteriorate electrical components over time. These outcomes can lead to costly repairs or replacements.
Proper Use and Maintenance of Ground Fault Protection Systems
Now that we understand the dangers associated with ground faults, we also must understand the importance of proper use and regular maintenance of Ground Fault Protection Systems in order to effectively mitigate these risks.
Proper Installation
Without the correct installation, Ground Fault Protection Systems will not function as intended. This could leave the electrical system, as well as workers, vulnerable to the above-mentioned hazards.
Regular inspection and testing
Regularly inspecting and testing the Ground Fault Protection System is key to ensure its effectiveness. Faulty components should be identified and swiftly replaced to avoid the risks that come with inadequate protection.
Training workers
Awareness and understanding among the construction workers handling electrical equipment are crucial. Proper training regarding the understanding, handling, and maintenance of these systems can further enhance safety.

Detecting Earth Faults
Identifying the presence of a ground fault is a crucial aspect of the ground fault protection system.
But how exactly do you figure out that there is a fault?
This segment takes you through the process of detecting earth faults, highlighting relevant indicators.
Acknowledging the Signs of Ground Faults
Ground faults may not always be obvious. However, recognising their indicators can help ensure immediate attention and resolution, thus preventing accidents and failures in the electrical system.
Unexpected Power Interruptions
Any unanticipated power interruptions can be a sign of a potential ground fault. If your ground fault protection system or Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) suddenly cuts off the power supply, it’s likely detecting a fault in the system.
Shock or Tingling Sensation
A strong indication of a potential ground fault is when there’s a shock or tingling sensation upon touching an electrical device or machinery. It signifies that electricity is escaping its normal pathway and is being conducted through the device’s body leading back to the ground.
Flickering Lights
Flickering lights can signal a variety of electrical problems, including a ground fault. This occurs when the electrical current diverts its course, causing inconsistency in the power supply to the lighting fixtures.
Utilising Advanced Ground Fault Detection Techniques
Overcoming the dangers of earth faults demands efficient detection techniques and tools. These methods and technologies can significantly enhance the accuracy of detecting faults, thereby ensuring a high level of safety.
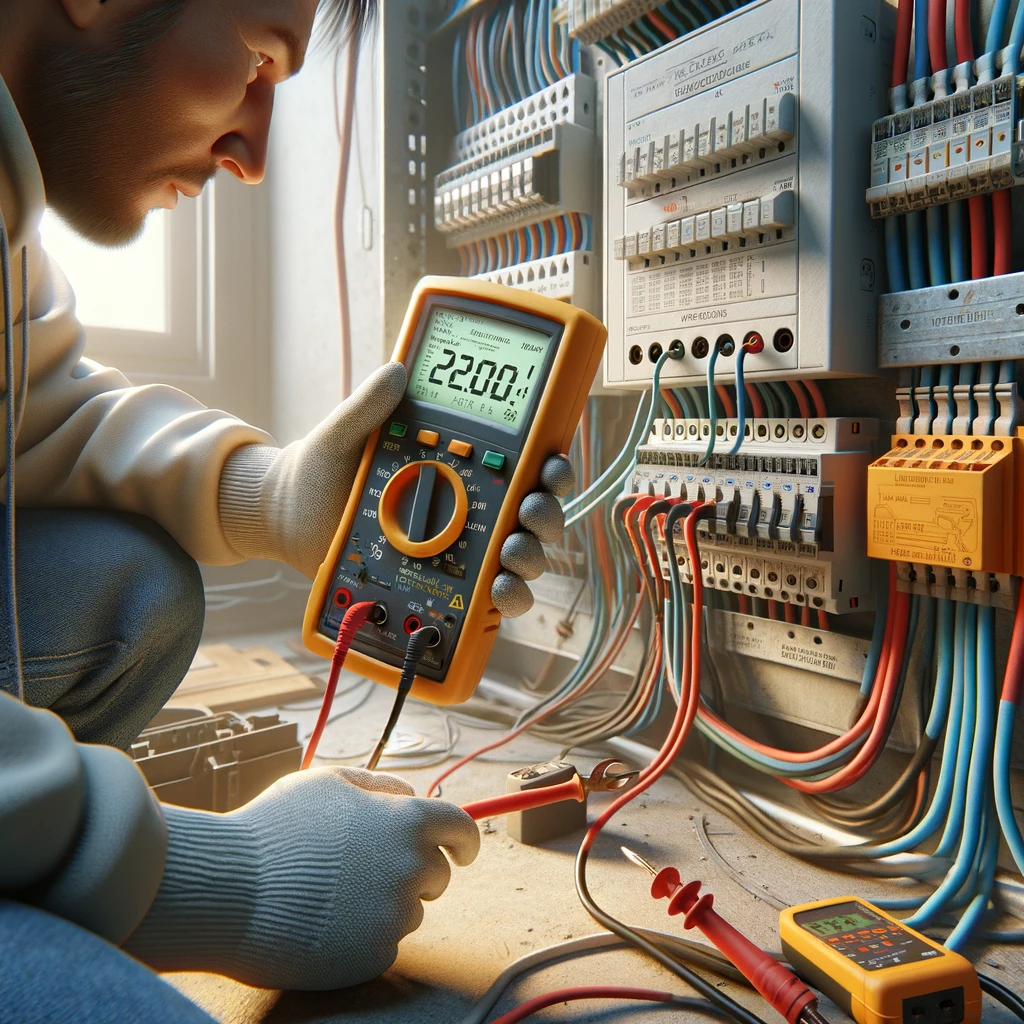
Use of Digital Multimeters
Professionals often resort to digital multimeters for detecting earth faults. A multimeter measures electric resistance and detects imbalances or disruptions in the current flow – a significant sign of a ground fault.
Infrared Thermography
Infrared thermography is increasingly used in detecting earth faults. It has the ability to identify overheating components in an electrical setup, often a result of loose connections or ground faults. Infrared cameras can detect the heat radiated from these areas, leading to a precise diagnosis.
Advanced Ground Fault Monitoring Devices
Certain advanced devices are designed specifically for monitoring earth faults. Skilled individuals typically install these in electrical installations and networks for regular monitoring of the electrical system’s health.
Importance of Professional Help
Ground faults present severe risks, understanding their causes, recognising the signs, and effectively addressing them requires professional expertise. It is recommended to have reliable electricians or electrical engineers inspect and test your electrical systems regularly to identify any possible faults and take corrective actions.
Knowing how to detect earth faults is an integral part of maintaining safety in any environment that interacts with electrical systems. Regular monitoring and prompt attention to signs can help prevent accidents and equipment damage.
Modern technology and professional help further assist in effectively locating and addressing these faults. Overall, a well-designed ground fault protection system protects people, promotes seamless operation, and extends the lifespan of your electrical installation.

Enhancing Safety with Ground Fault Protection Systems
Technology Behind Ground Fault Protection Systems
The ground fault protection system is equipped with advanced technologies to ensure optimal performance in detecting and managing faults. Let’s look at some key technologies integrated into these systems:
Evolving Sensing Technology
Ground fault protection systems include current transformers or sensors that continually monitor the electrical current passing through them. These sensors are designed to detect the slightest imbalance in the current that might indicate a leakage or ground fault, triggering the protection mechanism.
Sophisticated Anomaly Detection
Advancements in signal processing have played an essential role in improving the anomaly detection capabilities of ground fault protection systems. Complex algorithms are extensively used to differentiate between normal and abnormal activities within an electrical system.
Smart Interrupting Mechanism
Upon detection of a fault, modern ground fault protection systems are programmed to promptly interrupt the flow of electricity. This timely interruption prevents potential risks of electrocution and fires.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning have also found their way into ground fault protection. By analyzing historical patterns of current behavior, these devices can predict potential faults even before they occur, enhancing the overall detection and prevention measures.
The Influence of IoT in Ground Fault Protection
The rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) has created an opportunity for more refined ground fault detection and protection mechanisms.
Continuous Monitoring with IoT
IoT devices provide real-time monitoring of electrical systems, constantly tracking the flow of current. Continuous monitoring allows for faster detection of ground faults, thereby significantly reducing the risks associated with electrical hazards.
Remote Alerts and Controls
Moreover, with IoT enabled devices, alarms and notifications can be sent to smartphones or computers as soon as a ground fault is detected, providing an additional layer of safety. There is also the potential opportunity to manage and control the electrical equipment remotely.
Future of Ground Fault Protection Systems
With incredible advancements in technology, the future of ground fault protection systems is certainly promising. Researchers and developers worldwide are working on integrating more sophisticated technologies to create smarter, more proactive systems.
As technological advancements continue to evolve, so does safety equipment like ground fault protection systems. They are no longer passive safety mechanisms, but rather active walls of defense that monitor, predict, and alert about potential dangers.
The integration of these advanced technologies in ground fault protection systems certainly adds a crucial layer of protection in the construction industry and other electrical system-reliant sectors. This is heading towards a future where electrical safety is not left to chance but is reliably predictable and effectively manageable.
A Brief Roundup On Ground Faults
By constantly maintaining an equilibrium of electrical currents and promptly responding to ground faults, it significantly enhances safety and efficiency.
The system, constituted with key components like the Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI), circuit breaker, and grounding conductor, reduces the risk of electrical shocks and fire hazards.
From our perspective, being familiar with such systems is crucial for anyone interacting with electrical setups.
Not only does it minimize risk and prevent costly damages, but it also fosters an overall safer and more productive working environment. The essence of the ground fault protection system underscores one simple truth – prevention is always better than cure, especially when it comes to matters of safety in construction.