An Introduction to English Bond Masonry
Today, we’re exploring the world of English bond masonry – a traditional and popular brickwork pattern recognized for its immense strength and classic aesthetic appeal.
I could throw a statistic here, saying “80% of traditional European buildings use English bond masonry,” but let’s keep it simple – there are a lot of buildings that use this bond!
In this comprehensive article, we’ll clarify English bond masonry, discussing its fundamentals, key characteristics, and the role it plays in constructing load-bearing walls, retaining walls, and traditional buildings.
But that’s not all!
Further, we’ll analyze the pros and cons of this bricklaying technique, and even put it under the microscope by stacking it up against other brick bonds. Finally, we’ll walk you through its nitty-gritty aspects, providing a deeper understanding of brick placement, its strength rationale, and many elements that make it a sustainable choice.
Get ready to grasp the building blocks of construction – quite literally!
Table of Contents
Understanding English Bond Masonry in Construction
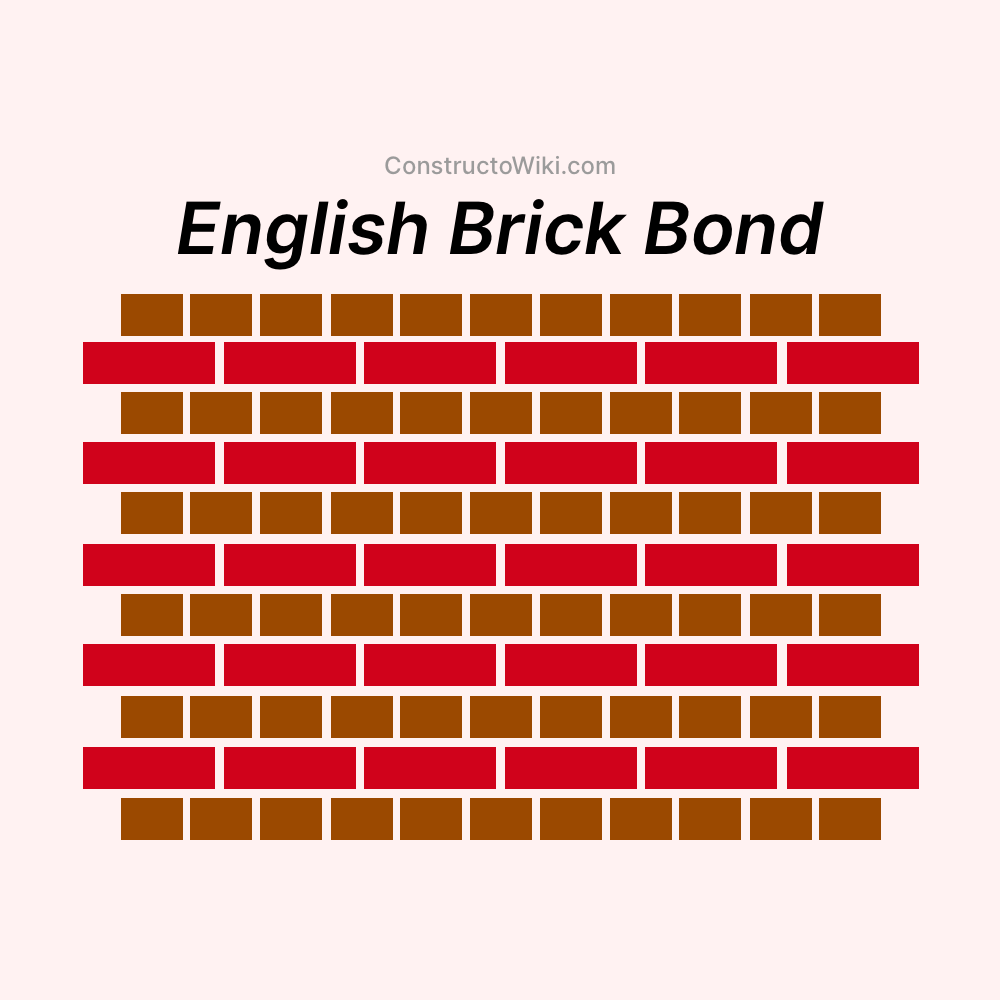
Defining English Bond Masonry
English bond masonry is a popular brickwork pattern used in construction, particularly for creating sturdy walls. It alternates between courses (or layers) of stretchers and headers. This method ensures strong interlocking between the bricks, producing durable and resilient walls.
Key Features of English Bond Masonry
- Alternating Courses: The pattern alternates with one course of stretchers (bricks laid longways), followed by one course of headers (bricks laid shortways).
- High Strength: This bond offers excellent structural integrity, making it suitable for load-bearing walls.
- Visual Consistency: Provides a uniform and traditional brick appearance, often preferred for its aesthetic value.
Applications of English Bond Masonry
- Load-Bearing Walls: Due to its strength, English bond is ideal for constructing walls that support structural loads.
- Retaining Walls: Its robustness makes it suitable for walls that need to resist lateral pressures from soil or other materials.
- Historic Buildings: Commonly used in the construction of older or historic buildings, preserving the traditional architectural style.
Advantages of Using English Bond Masonry
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Structural Integrity | English bond creates a high-strength wall suitable for various structural applications. |
| Aesthetic Appeal | This pattern offers a classic and uniform look, valuable for traditional architectural designs. |
| Durability | The alternating courses enhance the wall’s ability to withstand different types of stress. |
Disadvantages of Using English Bond Masonry
| Disadvantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Material Usage | English bond tends to use more bricks and mortar compared to other patterns, making it potentially more costly. |
| Labor Intensive | The precise laying of stretchers and headers can be time-consuming and require skilled labor. |
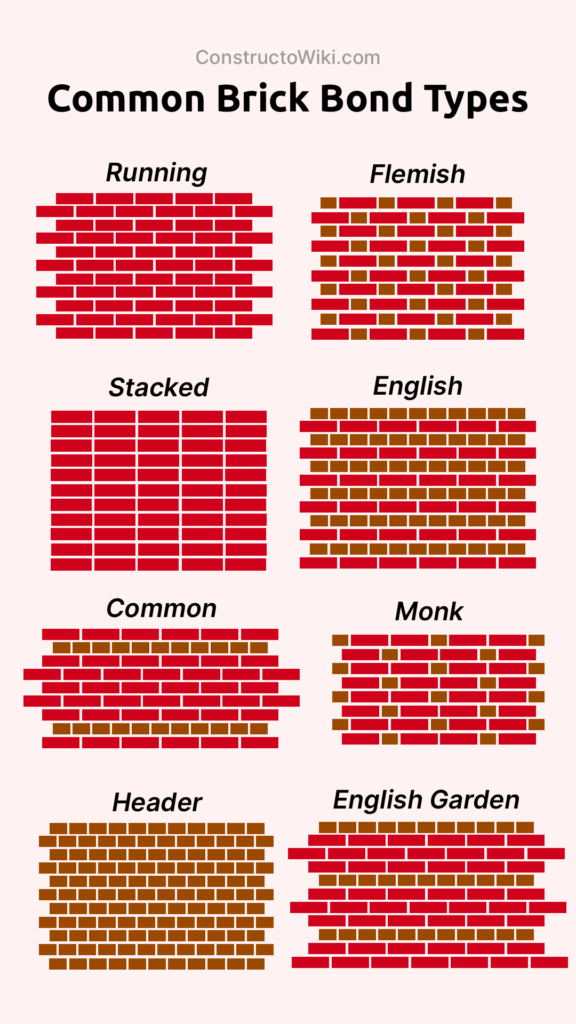
Comparing English Bond with Other Brick Bonds
| Brick Bond | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|
| English Bond | Alternates between stretchers and headers; high strength. |
| Flemish Bond | Alternates stretchers and headers in each course; decorative. |
| Stack Bond | All stretchers aligned vertically; less structural strength. |
Jumping into the Nitty-Gritty of English Bond Masonry
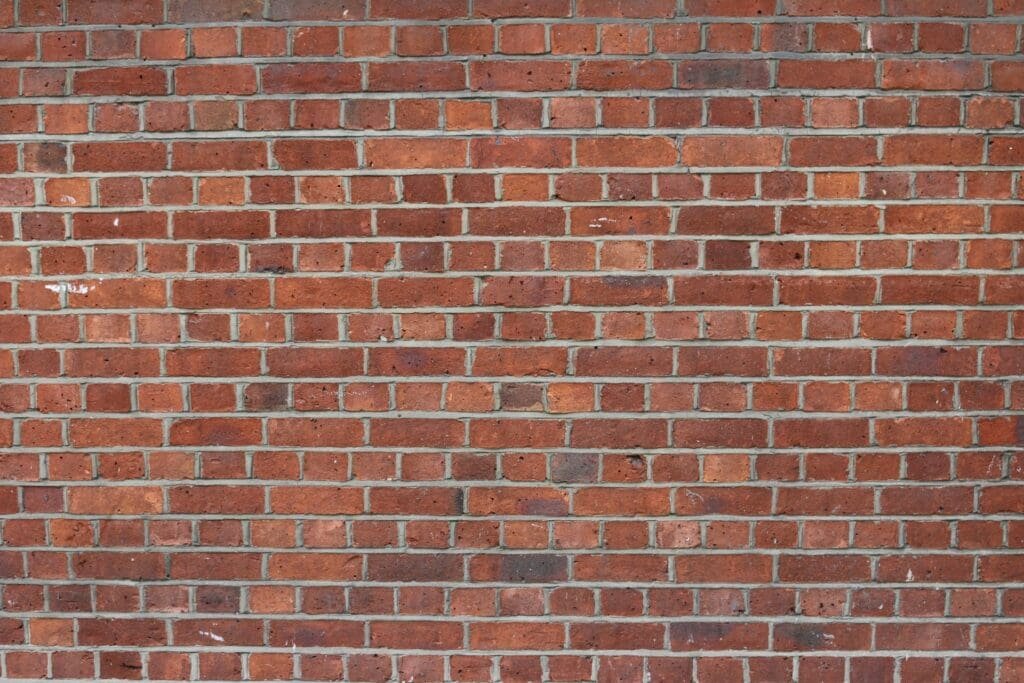
Elaborating on English Bond Masonry’s Brick Placement
In an English Bond pattern, the alignment of bricks enhances stability. “Courses” refer to rows of bricks; a header course contains bricks positioned widthways with their ends (or ‘headers’) facing out. Conversely, the stretcher course comprises bricks placed lengthways, showing their side (or ‘stretcher’) face. The pattern repeats after every alternate course – a header course follows a stretcher, and vice-versa. This neat arrangement ensures an efficient load distribution and a solid masonry wall.
Rationales Behind English Bond Masonry’s Strength
Brick bonds, especially English Bond, play a pivotal role in enhancing a masonry wall’s overall strength. But why is this specific bond considered sturdy?
This has lot to do with the alternating courses of headers and stretchers. The headers tie the wall’s thickness together, while the staggered stretchers prevent vertical cracks from forming. This combination creates an interlocked structure that can effectively withstand any applied loads, contributing to it being preferred in load-bearing constructions.
Sustainability through English Bond Masonry
Surprisingly, English Bond Masonry isn’t just about durability and aesthetics – it’s also a sustainable construction choice. This might seem counterintuitive, given its relatively high material usage. However, the longevity and durability of buildings constructed with English bond can often outweigh the initial resource expenditure, especially when considering long-term lifecycle costs.
Additionally, this bond’s thermal mass properties can offer energy efficiency benefits. Buildings constructed using high-density materials, like brick, can absorb, store, and gradually release heat, reducing the need for artificial heating and cooling.
Preservation and Restoration of Historic Buildings
In terms of historical preservation, English Bond Masonry plays an instrumental role. It’s frequently seen in listed buildings and other structures of historical significance, in part due to its traditional aesthetic appeal but primarily because of its inherent strength and durability. Conservationists and restorers well-versed in this bond can successfully maintain a building’s originality while also preserving its structural integrity.
Exploring Variations of English Bond Masonry
While traditional English Bond alternates courses of stretchers and headers, slight variations in the pattern allow masons to adapt to different architectural requirements. This flexibility in arrangement helps to circumnavigate potential problems during construction, including the alignment of doors and windows, or the need to support openings with lintel.
Enhancement of Structural Performance with English Bond
Regarded for its stoutness, English bond masonry is in itself a structural machine, bearing and transferring loads effectively. Rather than relying solely on piers or columns for support, the continuous usage of headers across the wall’s breadth facilitate the distribution of load, ultimately enhancing a building’s overall performance.
Differences Between Dutch Bond and English Bond Masonry
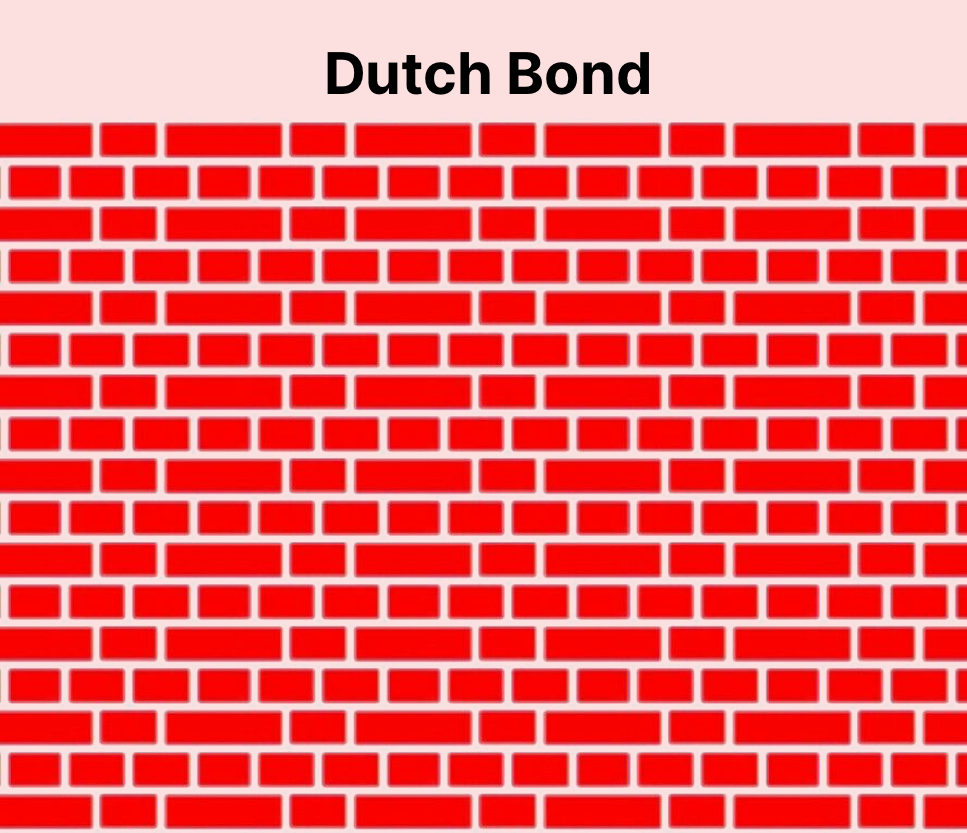
Defining Dutch Bond Masonry
Dutch bond masonry, while less commonly cited than other bonds, offers a fascinating alternative to traditional bonds. Dutch bond combines aspects of both English and Flemish bond patterns but introduces unique characteristics for enhanced aesthetic and structural performance. It features a stretcher course where stretchers align horizontally, followed by a header course mixed with headers and stretchers, providing a distinctive visual texture.
Key Features of Dutch Bond Masonry
- Mixed Header and Stretcher Courses: Dutch bond alternates a full course of stretchers with a course combining headers and stretchers. This creates a visually engaging pattern.
- Enhanced Aesthetics: The mixed header and stretcher courses offer a varied and textured appearance, ideal for decorative purposes.
- Moderate Strength: Provides a balance of structural integrity and aesthetic appeal, making it suitable for non-load-bearing walls.
Comparing English Bond and Dutch Bond Masonry
| Characteristic | English Bond | Dutch Bond |
|---|---|---|
| Brick Alignment | Alternates courses of stretchers and headers | Alternates stretcher courses with mixed courses of headers and stretchers |
| Aesthetic Appeal | Traditional, uniform appearance | Decorative, textured look |
| Structural Use | High structural strength, ideal for load-bearing walls | Moderate strength, typically used for decorative and non-load-bearing walls |
Advantages of Dutch Bond Masonry
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Aesthetic Versatility | The mixed header and stretcher pattern creates a varied and visually appealing look, suitable for decorative walls. |
| Moderate Resource Usage | Uses fewer bricks and mortar compared to English bond, potentially reducing material costs. |
Disadvantages of Dutch Bond Masonry
| Disadvantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Lower Structural Strength | Not as strong as English bond, making it less suitable for load-bearing applications. |
| Complexity in Construction | The pattern’s variation requires meticulous planning and skilled craftsmen to execute correctly. |
Applications of Dutch Bond Masonry
- Decorative Walls: Its visual texture makes it excellent for feature walls or facades.
- Residential Buildings: Suitable for non-load-bearing partitions and walls in homes where aesthetics are prioritized.
- Historical Renovations: Sometimes used in the restoration of historical buildings that originally featured such patterns.
For a deeper dive into the specifics of different brick bonds and their applications, visit The Constructor.
Wrapping Up: A Detailed Look into English Bond Masonry
English bond masonry stands out as a go-to strategy for constructing sturdy and visually consistent walls, making it a favorite in both modern and historical buildings. The alternating courses of headers and stretchers, besides providing a uniform facade, contribute to its strength and resilience.
This makes English bond an excellent option for load-bearing structures.
Despite its high material usage and labor intensity, buildings constructed using this bond promise long-term durability, aesthetic appeal, and sustainable benefits, such as energy efficiency. While there are other brick bonds, like Dutch bond, each has unique strengths, making them suitable for different structures.
Ultimately, a deeper understanding of brick bonds can enhance the artistry and sustainability of masonry construction.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is English bond masonry?
English bond masonry is a popular brickwork pattern that alternates between courses of stretchers (bricks laid longways) and headers (bricks laid shortways). This technique ensures strong interlocking between the bricks, producing durable and resilient walls.
What are the key features of English bond masonry?
English bond masonry is known for its alternating courses, high structural strength, and visual consistency. The uniform and traditional brick appearance makes it a favorite in both modern and historical architecture.
Why is English bond masonry suitable for load-bearing walls?
The interlocked structure of English bond masonry, created by alternating courses of headers and stretchers, can effectively withstand applied loads, making it an excellent choice for load-bearing constructions. Despite its high material usage, the long-term strength and durability often outweigh the initial resource expenditure.
How does English bond masonry compare with other brick bonds, such as the Dutch bond?
Each brick bond has unique strengths, making them suitable for different structures. While English bond is known for its high structural strength and suitable for load-bearing walls, Dutch bond, which combines aspects of English and Flemish bond, offers a balance of structural integrity and aesthetic appeal, making it suitable for non-load-bearing and decorative walls.






